Bionics»
Novel bio-inks can be used to print various types of tissue
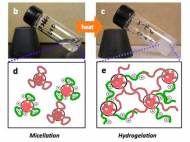
 A group of researchers at the Fraunhofer Institute have succeeded in developing bio-inks for tissue printing technology. The transparent liquids consist of components from the natural tissue matrix and living cells, such as a well known biological material – gelatin. By controlling the chemical modification of this biomolecule, researchers can imitate the properties of various… »
A group of researchers at the Fraunhofer Institute have succeeded in developing bio-inks for tissue printing technology. The transparent liquids consist of components from the natural tissue matrix and living cells, such as a well known biological material – gelatin. By controlling the chemical modification of this biomolecule, researchers can imitate the properties of various… »